Solved Problem on Relative Motion
advertisement
The wheel of radius R = 15 cm in the figure rolls, without slipping, parallel to a vertical
plane. The center C of the wheel has speed v = 5 m/s. What is the magnitude of the
velocity at point B in the following cases:
a) Diameter AB is normal to the running surface;
b) Diameter AB is parallel to the rolling plane.
a) Diameter AB is normal to the running surface;
b) Diameter AB is parallel to the rolling plane.

Problem data:
- Speed of the center of the wheel relative to the ground: v = vC = 5 m/s.
a) Since all points on the wheel move with the same speed from the center, we have that the magnitude of
the velocity at point B relative to the center of the wheel is also
vB/C = 5 m/s (if the speed were different some points would go faster than others and
the wheel would deform).
If the diameter AB is normal to the rolling plane, we can have two cases (Figure 1).
If the diameter AB is normal to the rolling plane, we can have two cases (Figure 1).
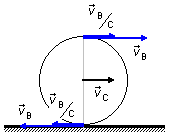
Figure 1
- Point B is at the bottom of the wheel in contact with the ground, and the velocity vector at
point B is opposite to the velocity vector at the center of the wheel, so the magnitude of
the velocity of point B with respect to the ground will be
\[ \begin{gather} v_{\small B}=v_{\small C}-v_{\small{B/C}}\\[5pt] v_{\small B}=5-5 \end{gather} \]\[ \begin{gather} \bbox[#FFCCCC,10px] {v_{\small B}=0} \end{gather} \]
- Point B is at the top of the wheel, and the velocity vector at point B has the same
direction as the velocity vector at the center of the wheel, so the magnitude of the velocity of
point B with respect to the ground will be
\[ \begin{gather} v_{\small B}=v_{\small C}+v_{\small{B/C}}\\[5pt] v_{\small B}=5+5 \end{gather} \]\[ \begin{gather} \bbox[#FFCCCC,10px] {v_{\small B}=10\;\mathrm{m/s}} \end{gather} \]
b) If the diameter AB is parallel to the running plane, then the velocity vector at point
B with respect to the center,
\( v_{B/C} \),
is perpendicular to the velocity vector at the center of the wheel,
\( v_{C} \),
(Figure 2), and the magnitude of the velocity at point B with respect to the ground,
\( v_{B} \),
will be given by the Pythagorean Theorem.
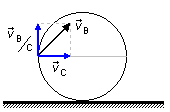
\[
\begin{gather}
v_{\small B}^2=v_{\small C}^2+v_{\small{B/C}}^2\\[5pt]
v_{\small B}^2=5^2+5^2\\[5pt]
v_{\small B}^2=25+25\\[5pt]
v_{\small B}=\sqrt{50\;}
\end{gather}
\]
\[
\begin{gather}
\bbox[#FFCCCC,10px]
{v_{\small B}=7.1\;\mathrm{m/s}}
\end{gather}
\]
advertisement

Fisicaexe - Physics Solved Problems by Elcio Brandani Mondadori is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .