Solved Problem on Relative Motion
advertisement
On a windless rainy day, the rain falls vertically to the ground at a speed of 10 m/s. A car moves horizontally with a constant speed of 72 km/h relative to the ground.
a) What is the direction of the rain relative to the car?
b) What is the speed of the rain relative to the car?
Problem data:
- Car speed relative to the ground: vc = 72 km/h;
- Rain speed relative to the ground: vr = 10 m/s.
Solution
First, we must convert the car speed given in kilometers per hour (km/h) to meters per second (m/s) used in the International System of Units (SI)
\[
\begin{gather}
v_c=72\;\frac{\;\mathrm{\cancel{km}}}{1\;\mathrm{\cancel{h}}}\times\frac{1\;\mathrm{\cancel h}}{3600\;\mathrm s}\times\frac{1000\;\mathrm m}{1\;\mathrm{\cancel{km}}}=\frac{72}{3.6}\;\mathrm{\frac{m}{s}}=20\;\mathrm{m/s}
\end{gather}
\]
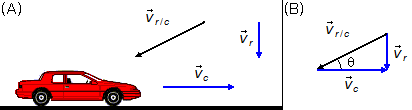
a) The problem gives us legs
\( {\vec v}_r \)
and
\( {\vec v}_c \)
(Figure 1-A). We want to find the direction given by the angle θ, the tangent of the
angle θ will be (Figure 1-B)
\[
\begin{gather}
\tan \theta =\frac{\text{opposite leg}}{\text{adjacent leg}}=\frac{v_a}{v_c}=\frac{10\;\mathrm{\cancel{m/s}}}{20\;\mathrm{\cancel{m/s}}}=\frac{1}{2}
\end{gather}
\]
From the Trigonometry the angle θ will be the arc whose tangent is
\( \frac{1}{2} \)
\[
\begin{gather}
\theta =\arctan \left(\frac{1}{2}\right)=26.5°
\end{gather}
\]
\[
\begin{gather}
\bbox[#FFCCCC,10px]
{\theta=26.5°}
\end{gather}
\]
b) The magnitude of the velocity of the rain relative to the car is represented by \( {\vec v}_{r/c} \), (Figure 1-A). The magnitude of the velocity of the rain relative to the car will be obtained by applying the Pythagorean Theorem to the triangle in Figure 1-B. The magnitude of \( {\vec v}_{r/c} \) represents the hypotenuse of the triangle, which we want to find, and the magnitudes of \( {\vec v}_r \) and \( {\vec v}_c \) are the given legs
\[
\begin{gather}
\bbox[#99CCFF,10px]
{{\vec v}_r={\vec{v}}_{r/c}+{\vec v}_c}
\end{gather}
\]
the magnitude will be
\[
\begin{gather}
v_{r/c}^2=v_a^2+v_c^2\\[5pt]
v_{r/c}^2=(10\;\mathrm{m/s})^2+(20\;\mathrm{m/s})^2\\[5pt]
v_{r/c}^2=100\;\mathrm{m^2/s^2}+400\;\mathrm{m^2/s^2}\\[5pt]
v_{r/c}=\sqrt{500\;\mathrm{m^2/s^2}\;}
\end{gather}
\]
\[
\begin{gather}
\bbox[#FFCCCC,10px]
{v_{r/c}=22.4\;\mathrm{m/s}}
\end{gather}
\]
advertisement

Fisicaexe - Physics Solved Problems by Elcio Brandani Mondadori is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .